EXPERTISE // SERVICES // METALLURGY AND APPLIED MECHANICS
Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis
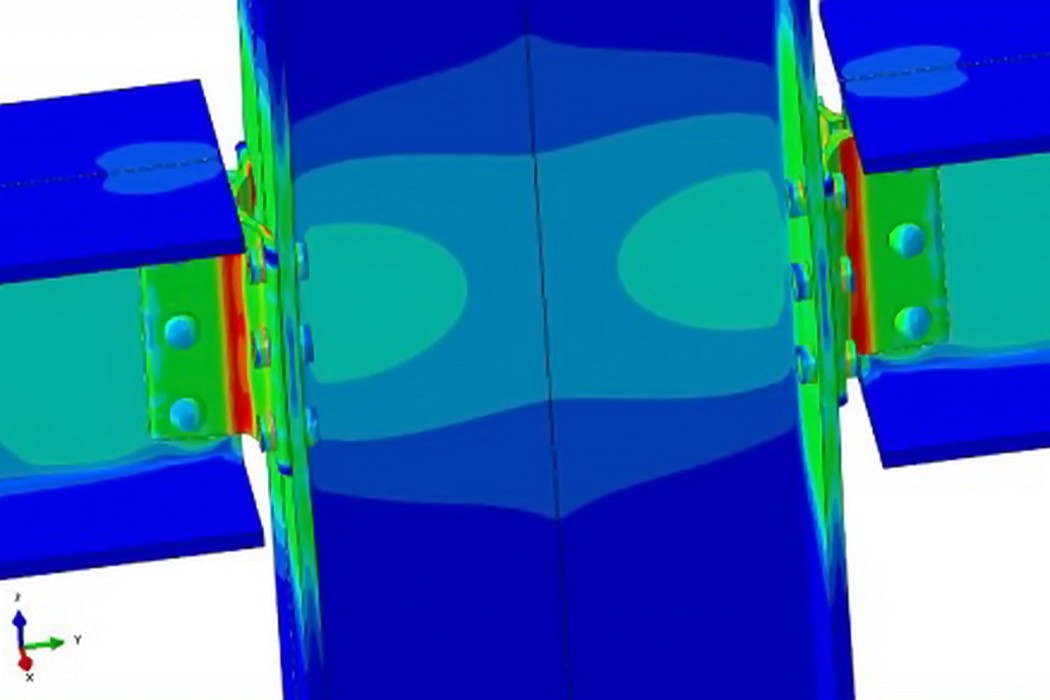
Having investigated and consulted on hundreds of structures and pressurized equipment components, our professionals are experienced providers of specialty nonlinear finite element modeling services for all types of new and existing solid components. We leverage recognized industry techniques, advanced academic preparation, and years of experience to provide rapid assessment and actionable, cost-effective solutions for challenging new designs, existing infrastructure, and unexpected failures.
Clients seek nonlinear finite element analysis to provide predictions for complex systems where traditional engineering methods are not well-suited, large numbers of tests are impractical, and/or sensor access is limited. We conduct most analyses with the commercial software program Abaqus; however, we maintain several other programs that are built for specific applications. We use the latest hardware and draw on years of experience to minimize model run-times and to achieve the right level of analysis sophistication for our clients’ needs. In addition to quantitative capabilities, we emphasize strong mechanical qualitative reasoning among our analysts, who work closely with laboratory and field instrumentation engineers to provide holistic solutions.
We primarily focuse on structures and pressure-containing equipment such as bridges, cranes, buildings, pipelines, piping, tanks, pressure vessels, railroads, pavement, foundations, offshore structures, and mechanical equipment. We maintain the most up-to-date knowledge in modeling techniques for metals, elastomers, granular materials, and reinforced concrete and offer independent, third-party reviews.
- Fracture mechanics assessment and fitness-for-service
- Plasticity and other material nonlinearity
- Geometric nonlinearity and buckling
- Vibration
- Explicit dynamics, impact, and blast
- WJE CrackCalc™ (API 579 Fracture Mechanics Software)
- Complex multibody assemblies with contact
- Thermomechanical response
- Hydraulically actuated systems
- Reinforced concrete
- Granular materials
- Peer review
RELATED INFORMATION
-
 WJE's Janney Technical Center (JTC) provides advanced testing and forensic capabilities to... MORE >Labs | Janney Technical Center
WJE's Janney Technical Center (JTC) provides advanced testing and forensic capabilities to... MORE >Labs | Janney Technical Center -
 Our metallurgical and applied mechanics engineers provide solutions related to design... MORE >Services | Metallurgy and Applied Mechanics
Our metallurgical and applied mechanics engineers provide solutions related to design... MORE >Services | Metallurgy and Applied Mechanics -
 Our engineers routinely test materials and systems to failure under controlled conditions MORE >Services | Structural Load and Fatigue Testing
Our engineers routinely test materials and systems to failure under controlled conditions MORE >Services | Structural Load and Fatigue Testing